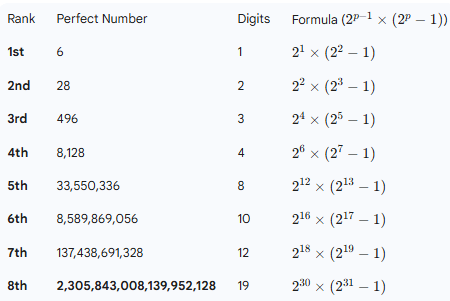
Explores perfect numbers, defined as positive integers equal to the sum of their proper divisors. Examples include 6, 28, and 496, with only 52 known today. It discusses mathematical properties, unsolved questions about odd perfect numbers, historical significance, and the connection to Mersenne primes, highlighting their allure across centuries.